
What are the benefits of Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is essential for human health, and sunlight is the natural source of vitamin D. This vitamin is a family of compounds that includes D1, D2, and D3. It is also known as Calciferol, a fat-soluble vitamin. Other than sunlight, it is also present in some food and supplements.
Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory effects on cancerous cells. In carcinogenesis, cancerous cells may induce inflammation in the early stages. The immunoregulatory effects of vitamin D can inhibit cancer. It also promotes modulation of immune function, cell growth, and neuromuscular.
Nowadays, many people are affected by the deficiency of vitamin D. Research supports the claim that vitamin D supplements can improve heart function in the body. Bones and joints can also strengthen with the help of vitamin D. It helps our bodies regulate calcium and phosphate levels. It gives the healthy nutrients that keep the bone, teeth, and muscles healthy.
Researchers are conducting multiple research trials to identify the role of vitamin D in other diseases. Various studies have shown that Vitamin D can affect other diseases and conditions to improve.
Taking Vitamin D with Omega 3, which contains EPA and DHA, can improve 25OHD levels in your body. EPA and DHA contribute to the normal functioning of the heart by decreasing blood pressure and heart rate, reducing inflammation in arteries, and increasing elasticity in heart chambers.
What are the primary sources of Vitamin D?
Skin is the essential part of the body, responsible for producing Vitamin D with exposure to sunlight and UV rays.
According to a study in 1980, vitamin D synthesis starts with seven dehydrocholesterol, a particle that is present in the skin but in the lowermost layer of the epidermis. After this process, ultraviolet B radiation enters the skin, making 7-DHC into an isomer; this spatial configuration of atoms is called preD3. Lastly, the skin temperature is responsible for the reaction of isomerization and preD3.
In the case of over-concentrated isomerization, the chemical reaction will be forced into equilibrium and stops the vitamin D3 synthesis.
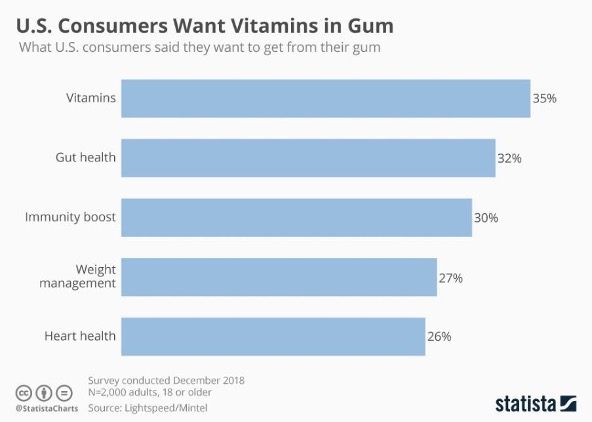
Source: Statista
Vitamin D3 plays a fundamental role in mineralizing the bone system at all ages and for all genders. Food can help cope with the deficiency of Vitamin D and supplements. People like to chew gum containing vitamins and energy boosters.
- Below is the list of foods that are rich in Vitamin D.
- Cod liver oil
- Canned tuna
- Egg yolks
- Mushrooms
- Dairy and plant milk
- Orange juice
- Salmon
- Swordfish
Deficiency of Vitamin D
One billion people around the globe suffer from Vitamin D deficiency, which includes 14 to 59% of adults. Vitamin D deficiency is most prevalent in Asian countries.
There is a high possibility of deficiency of sunshine vitamin (Vitamin D) if a person shuns the sun and suffers from milk allergies. The main target of this vitamin is to make the bones strong. People having issues related to bone pain or muscle weakness may have a vitamin D deficiency.
Vitamin D deficiency in children can cause Rickets. This disease makes the bones soft and bendable and has dire effects on a child's life. However, in adults, the deficiency of Vitamin D can cause osteomalacia, which causes muscle weakness, bone pain and weakness in bones.
Other than this, deficiency of vitamin D is responsible for many other diseases such as:
- Asthma in children
- Cancer
- Heart disease
- Osteoporosis
- Osteomalacia
Recommended Doses of Vitamin D
Doctors recommend vitamin D supplements for all ages. The only difference in the recommendation is the dose.
Infants from 0-12 months need 400IU of Vitamin D. Children need 600 to 1000IU per day. Adults can handle 1500-2000 IU daily. While the dose changes in all stages of pregnancy. It usually varies from 1000 to 1500IU daily.
Vitamin D Toxicity
Taking an accurate dose of Vitamin D is necessary because overuse of Vitamin D supplements can cause Vitamin D toxicity. As vitamin D helps absorb calcium, vitamin D overdose can cause hypercalcemia. Hypercalcemia is a condition when calcium builds up in your blood.
The symptoms of vitamin D overdose are nausea, vomiting, weakness, bone pain, and kidney issues.
If the source of vitamin D in your body is the sun, you will not get vitamin D toxicity by sitting in the sun for long hours. Overuse of vitamin D supplements is the common cause of vitamin D toxicity.
You can increase your Vitamin D intake in the winters because the absence of sunlight restricts vitamin D production on our skin. Use supplements if winters last longer than usual in your country.













